Answers and Explanations to last week's Normal Distribution Quiz! #21
Quick revision of the basics!
Hello Everyone,
As promised earlier, in today’s newsletter, I am sharing the answers with brief explanations for the Normal distribution Quiz sent last week. You can cross check your answers with these answers to evaluate your performance.
Again an important reminder, understanding normal distribution basics is crucial for building effective and reliable statistical and machine learning models. So, make sure to dive deep into this topic. It’s one of the most favourite topics of interviewers.
Please feel free to add any additional comments related to any of the questions, answers and explanations. I have provided “Leave a comment” button after each one of them.
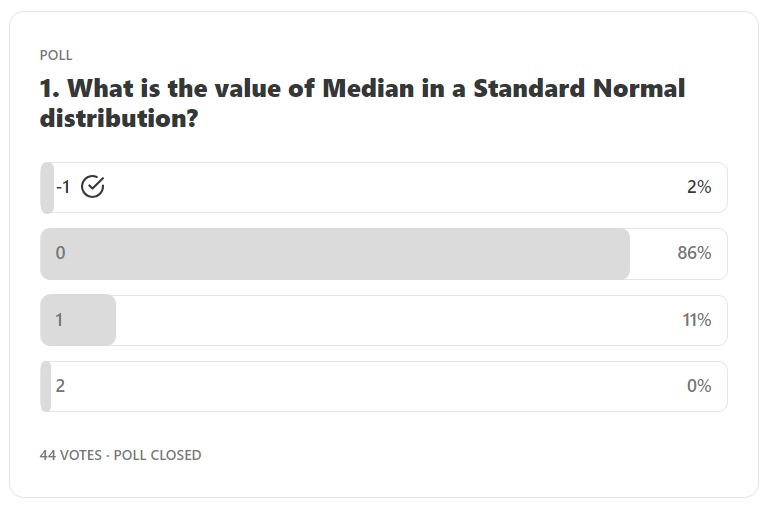
Answer: 0
Explanation: In a standard normal distribution, median is equal to the mean. Since mean value is 0, median value is also 0.
Answer: Is an outlier
Explanation: Z-score of 4 means the data point is 4 standard deviations above the mean. A per empirical rule, most of the data points lies within 3 standard deviations from the mean. So, this data point is an outlier.
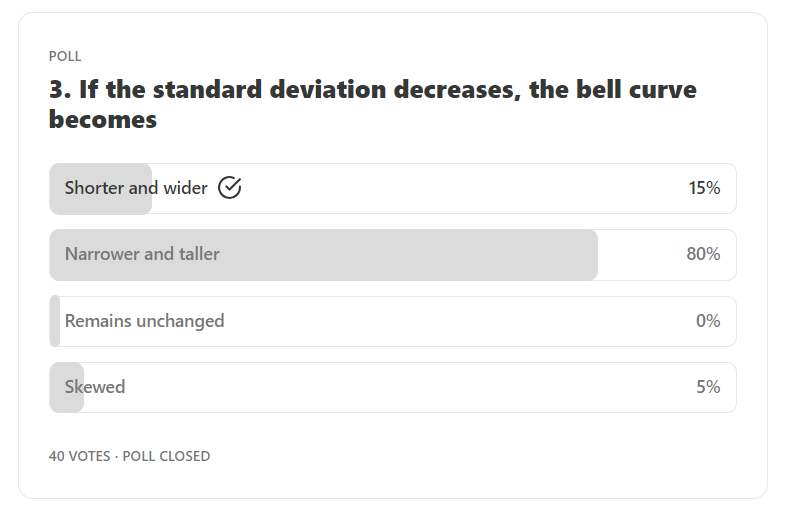
Answer: Narrower and taller
Explanation: Standard deviation tells the spread of the data points around the mean. If standard deviation decreases, the data spread decreases which make the curve narrower.
Now, the total area under the bell curve is 1. So, if the shape becomes narrow, the height of the peak should increase to maintain the same area. Thus, the curve become taller.
Answer: 0
Explanation: A normal distribution is a continuous distribution. In a continuous distribution, the probability at a single point is 0. So, if the data point is exactly equal to the mean, its probability will be 0.
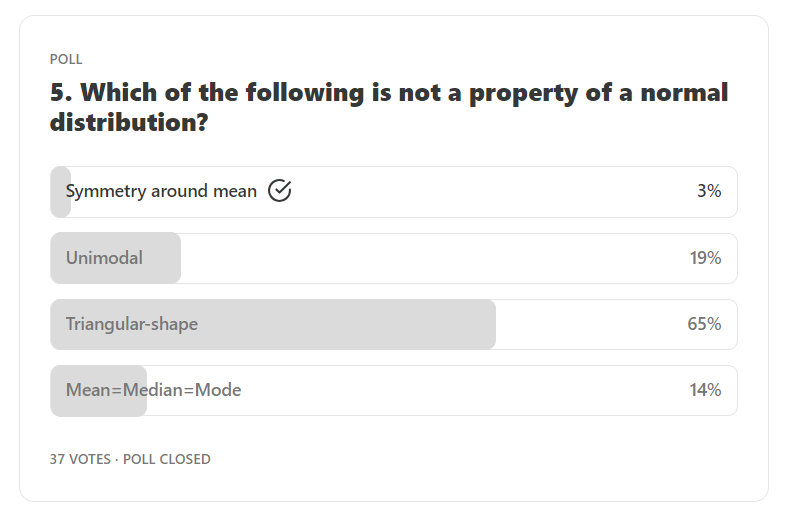
Answer: Triangular-shape.
Explanation: Symmetry around mean, Unimodal and Mean = Median = Mode are some of the key properties of a normal distribution. The shape of a normal distribution is not triangular, it’s bell shape.
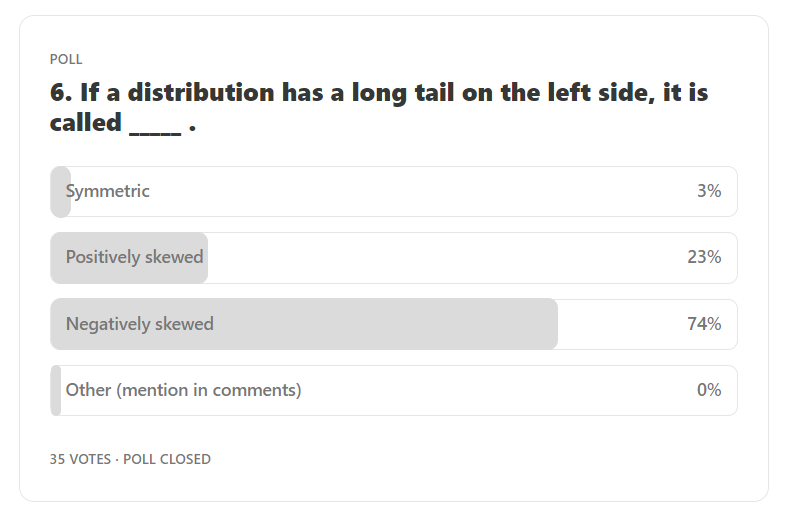
Answer: Negatively skewed
Explanation: Long tail on the left side means the distribution is negatively skewed. This is called negatively skewed because the skewness in this case is negative(<0).
If the long tail is on the right side, it is called positively skewed. The skewness in this case is positive (>0).
In a perfectly symmetric distribution, the skewness is 0.
Answer: mean> median> mode
Explanation: In a positively skewed distribution, there is a longer tail on the right side.
Since, mean is an average value, it is often influenced by the extreme values in the direction of the skew. In this case, the extreme values lies on the right tail. So, the mean gets pulled in that direction.
Median divides the data into two halves means one half of the distribution lies to its right side and the other half lies to its left side. So, the median remains unaffected by the extreme values. It lies between mean and mode which are sensitive to outliers.
Mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a distribution and therefore, the peak of the distribution lies at this point. In a positively skewed distribution, it lies to the left of median because the distribution is dense on the left side.
Answer: 0
Explanation: The peak of a standard normal distribution is located at the mean and mean = 0.
Answer: All of the above
Explanation: Q-Q Plot and Histogram are the visual/graphical methods to check the normality of a distribution while Shapiro Wilk test is the statistical method.
Answer: 95%
Explanation: I forgot to add approx. with the percentage values in the option. So, please consider this. As per empirical rule, in a standard normal distribution approx. 68% of the data lies between -1 and 1, approx. 95% of the data lies between -2 and 2 and approx. 99.7% of the data lies between -3 and 3.
Do you enjoy QUIZ newsletters?
Curious about a specific AI/ML topic? Let me know in comments.
Also, please share your feedbacks and suggestions. That will help me keep going. Even a “like” on my posts will tell me that my posts are helpful to you.
See you soon!
-Kavita
P.S. Let’s grow our tribe. Know someone who is curious to dive into ML and AI? Share this newsletter with them and invite them to be a part of this exciting learning journey.